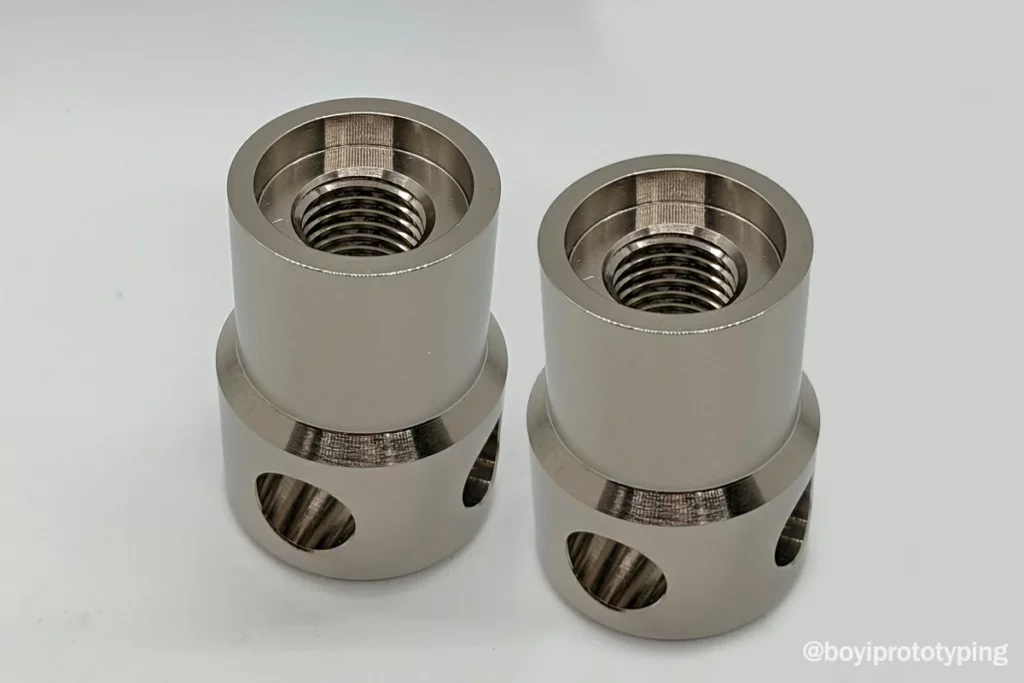
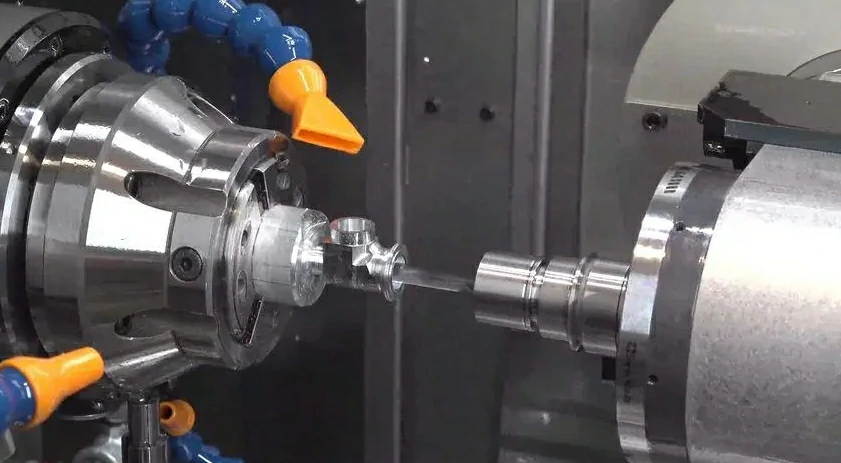
What is CNC Turning, Really?
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. In simple terms, CNC turning is a manufacturing process in which a piece of material (metal, plastic, etc.) is held in a chuck and rotated while a cutting tool is brought against it to remove material, shaping it into the desired form. This process is carried out by a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathe, which is programmed to execute precise movements and cuts based on a digital design file.
The result? Parts that are consistently within tight tolerances, perfectly aligned with your specifications, and ready for whatever application you have in mind.
What Are the 8 Parts of a CNC Turning Machine?
- Headstock: Holds the workpiece and powers the spindle.
- CNC Lathe Bed: The stable base that supports the machine.
- Chuck: Clamps the workpiece at the center of rotation.
- Tailstock: Supports the far end of the workpiece.
- Tailstock Quill: Holds and positions tools for drilling.
- Foot Pedals: Controls machine functions hands-free.
- CNC Control Panel: Interface for programming and control.
- Tool Turret: Automatically rotates and positions cutting tools.
To identify the parts of a CNC turning machine, start by reviewing the user manual and breakdown images specific to your model. Understand each component, as names and layouts can vary between manufacturers. Refer to the machine’s diagram for the correct nomenclature according to the manufacturer.

How CNC Turning Parts Are Made?
The production of CNC turning parts starts with a detailed design created in CAD software, which is then translated into a CNC program. The right material is selected based on the part’s requirements, and the CNC lathe is set up with precise tools. The machine rotates the workpiece while cutting tools shape it according to the program, ensuring high precision. Quality checks are conducted throughout, and finishing touches like polishing or coating are applied if needed, resulting in a high-quality, precision-made part.
Why CNC Turning Parts Are Essential?
CNC turning parts are everywhere, from the small screws in your smartphone to the complex parts in automotive engines. Here’s why they’re so critical:
Versatility
CNC turning can handle a wide range of materials, including metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics. This versatility makes it suitable for producing parts for various industries, from electronics to automotive.
Precision
CNC turning allows for extremely tight tolerances, which means the parts produced are incredibly accurate. This is crucial in industries where even the smallest error can lead to failure, like in aerospace or medical fields.
Consistency
Once the CNC machine is set up, it can produce thousands of identical parts without any variation. This consistency is key in manufacturing, where uniformity can make or break the final product.
Efficiency
CNC turning is fast and efficient. Since the process is automated, it reduces the time required to produce parts and minimizes human error. This efficiency translates into lower costs and faster turnaround times.
Key Considerations When Choosing CNC Turning Parts
When you’re sourcing CNC turning parts, there are a few things you need to keep in mind to ensure you’re getting the best quality:
- Different materials have different properties—some are harder, others are more flexible, and some are more resistant to wear and tear. The right material depends on the part’s application.
- The finish of a CNC turned part is not just about aesthetics; it affects the part’s functionality too. For instance, a smoother finish can reduce friction in moving parts, leading to longer-lasting components.
- Depending on the application, you might need parts with very tight tolerances. Make sure to communicate your tolerance requirements clearly with your manufacturer to avoid any issues down the line.
- Whether you need a single prototype or a full production run, make sure your supplier can handle the volume. Some companies specialize in small batches, while others are geared for mass production.
- While CNC turning is cost-effective, prices can vary depending on the complexity of the part, the material used, and the quantity needed. It’s essential to balance cost with quality to get the best value for your money.

What Materials are Used in CNC Turning Parts?
Commonly used materials include metals like aluminum, stainless steel, brass, and titanium, which offer excellent strength and durability. Plastics such as ABS, nylon, and polycarbonate are also frequently used, especially when lightweight or corrosion-resistant parts are needed. The choice of material largely depends on factors like the part’s function, the required precision, and environmental considerations.
What is CNC Turning Terminology?
CNC turning terminology encompasses the specific language and key concepts associated with Computer Numerical Control Turning. This includes terms related to the machine’s components, the movements and speeds involved, and the precision of the cutting process.
Choosing the Right CNC Turning Partner
When you partner with the right CNC turning specialist, you gain more than just parts; you gain confidence in your products and their ability to perform under any circumstances.
Choose BOYI for your CNC machining services needs and benefit from precision-engineered solutions that deliver exceptional repeatability and quality. No matter the size of your project, our expert team and state-of-the-art equipment ensure your specifications are met with the highest standards. Contact us today to enhance your production efficiency and achieve superior results!

Let’s Start A New Project Today
Our engineers will contact you within 2 hours.
FAQ
Accuracy depends on the machine’s capabilities, tooling, and programming. Modern CNC turning centers can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005mm or even finer for some applications.
Absolutely, CNC turning is commonly used for rapid prototyping due to its ability to produce precise, complex parts quickly. This makes it ideal for verifying design concepts before committing to larger-scale production.
Quality assurance typically involves a combination of in-process inspections, final inspections using precision measuring tools, and possibly first article inspection (FAI) for new or modified designs. ISO certifications, such as ISO 9001, can also provide assurance that the manufacturer follows rigorous quality control procedures.
Common file formats for CNC programming include IGES, STEP, DXF, DWG, and, most importantly, CAM-specific formats like G-code. Providing 3D CAD models (e.g., STL, SolidWorks, AutoCAD) is typically the starting point, which is then converted into G-code by CAM software.
Catalog: CNC Machining Guide

This article was written by engineers from the BOYI team. Fuquan Chen is a professional engineer and technical expert with 20 years of experience in rapid prototyping, mold manufacturing, and plastic injection molding.