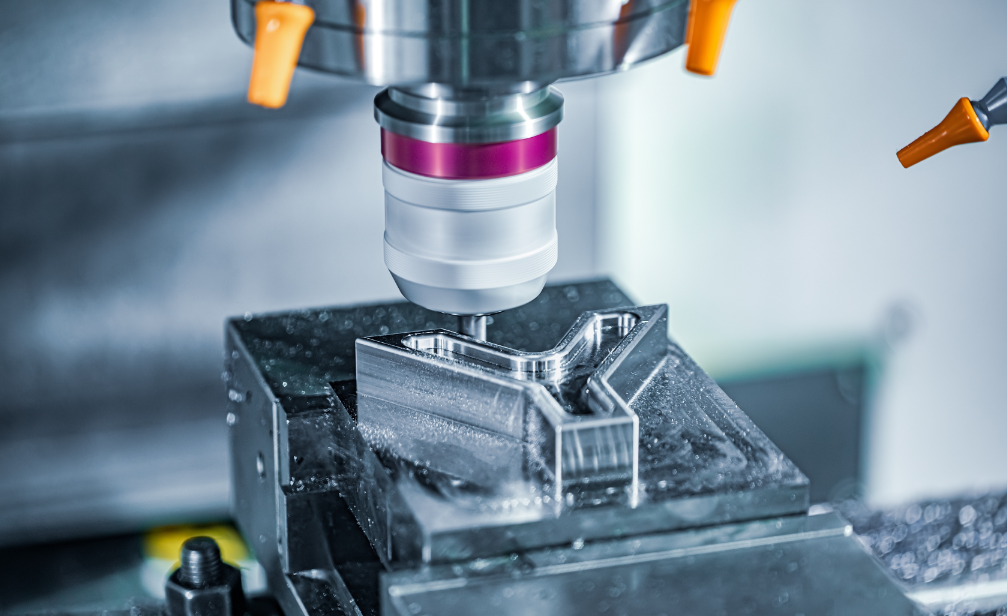
CNC machining (subtractive manufacturing) is one of the most common machining methods. Prototyping and small-batch production rely on the precision, dimensions, and cost advantages of CNC machining. Whether it’s metal, plastic, or wood, perfect processing can be achieved.
In fact, because plastic machining is more challenging than metal machining, the majority of manufacturers prefer CNC machining for metal products. However, with the introduction of computer numerical control, plastic CNC machining has become more precise, faster, and suitable for manufacturing parts with strict tolerances.
Plastic CNC machining may seem simple, but it involves many details and techniques. This article will analyze the techniques available in plastic CNC machining, the characteristics of common plastic materials, and their applications in plastic CNC machining to help you make informed decisions.
Can Plastic Be CNC Machined?

Yes, plastic can be CNC machined.This method is commonly used for prototyping, low-volume manufacturing, and even high-volume production of plastic components.
Plastics such as acrylic, ABS, nylon, polycarbonate, and many others can be CNC machined to produce parts for various applications ranging from prototypes to final products.Compared to metals, plastic materials have lighter weight, better insulation performance, and easier molding characteristics.
Related: CNC Machining Metal vs. Plastic: The Key Differences
Common Materials Used For Plastic CNC Machining
Most types of plastics can be used to manufacture plastic parts. However, different types of plastics are suitable for different applications due to their unique physical and chemical properties. Boyi suggests that everyone should use these materials according to their respective characteristics. Here are some common plastic processing materials and their characteristics and applications:
ABS

ABS is a polymer composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene terpolymers, favored by numerous industries for its wide applicability. It cleverly combines the performance characteristics of PS, SAN, and BS, demonstrating balanced and excellent toughness, hardness, and rigidity.
Color
White, black, and beige
Advantages
- It has outstanding chemical corrosion resistance and heat resistance, while maintaining excellent stability in the range of -50 to +70°C.
- It possesses high mechanical strength and rigidity, and is not easily scratched.
- It exhibits the processing characteristics of thermoplastic plastics.
- It is easy to color and process, and can also be plated.
- Excellent tensile strength and wear resistance.
Disadvantages
Not weather resistant, limited resistance to acid corrosion, soluble in ketones, and softens in certain chemicals (such as chlorinated hydrocarbons, fats, aromatic compounds, and aldehydes).
Applications
It is commonly used as a modeling material. Widely used in the automotive, electronics, and other industries to manufacture automotive dashboard components, converters, speakers, connectors, etc.
POM

POM, a homopolymer, is also known as Delrin(trade name). It is widely adopted as an engineering-grade thermoplastic for manufacturing prototypes for industrial purposes. It typically exists in two forms: copolymer or homopolymer. From intricate prototypes to resilient machine parts, it brings economic benefits to the manufacturing industry.
Color
Black, white
Advantages
- Resistant to organic solvents, does not dissolve at room temperature.
- Resistant to low temperatures, maintains toughness even at temperatures as low as -40°C.
- High compressive strength, second only to glass fiber.
- Excellent wear resistance and resistance to creep deformation.
Disadvantages
Not resistant to mineral acids. Additionally, it is not UV resistant, does not have self-extinguishing properties, cannot be close to a source of fire, and has weak resistance to impact.
Applications
Extensively used in the manufacture of mechanical equipment components such as bearings, worm gear, impellers, cams, washers, bushings, guides, handles, and grips. POM finds widespread applications in industries such as automotive, electronics, medical, and food machinery.
PMMA (Plexiglass/Acrylic)

PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate), also commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, is a highly plastic polymer material. This plastic polymer is renowned for its translucency and scratch resistance, thus finding widespread application in numerous industries requiring these characteristics.
Color
Colorless and transparent
Advantages
- Boasts excellent glossiness; its surface can be polished, with a high light transmittance of up to 92%, and a refractive index of 1.49, approaching the optimal optical glass performance.
- Resistant to erosion from inorganic acids, alkalis, hydrocarbons, and cleansers.
- Possesses excellent electrical and dielectric properties, as well as outstanding mechanical strength.
- Good resistance to UV radiation and weathering.
- Wide operating temperature range, from -40°C to 90°C.
Disadvantages
Susceptible to stress cracking; relatively poor chemical resistance and impact resistance. Relatively brittle, with mechanical properties effective in the short term; for long-term use, ensure tensile strength requirements are below 1500 psi to avoid brittle fracture. Its impact resistance is lower, and toughness decreases with decreasing temperature.
Applications
Commonly used for machine covers and parts, clock dials, fan blades, relay covers, and windshield components. Additionally, it is often utilized in the production of transparent models, specimens, ornaments, dentures, and advertising plaques.
PC(Polycarbonate)

PC (polycarbonate) is a colorless thermoplastic engineering material known for its amorphous, odorless, and non-toxic characteristics. Similar to acrylic, PC has become an ideal alternative to glass due to its inherent transparency.
Color
Colorless and transparent
Advantages
- Boasts outstanding impact resistance, toughness, and resistance to creep deformation.
- Can withstand climate change and high temperatures, stable for use in the range of -150°C to +120°C.
- Exhibits excellent flame resistance and radiation resistance.
- Good electrical insulation properties.
Disadvantages
Prone to scratching, difficult to polish, and relatively weak resistance to arcing. Long-term immersion in water can lead to embrittlement. Sensitive to indentation, prone to rupture at stress concentrations. Additionally, PC material reacts with hydrolysis, resulting in poor chemical corrosion resistance.
Applications
Commonly used as safety glass, projector equipment components, and materials in mechanical, electronic, automotive, and architectural fields. In the aerospace, electronics, and mechanical industries, PC materials are used for components such as windshields, bulletproof glass, and observation windows for instruments and meters.
Nylon(Polyamide)

Nylon is a high-performance engineering plastic with excellent mechanical properties, high impact resistance, chemical resistance, and abrasion resistance, making it highly suitable for plastic CNC machining.
Color
Natural, black, white
Advantages
Highly crystalline with polar groups on the molecular chain, imparting excellent mechanical strength and toughness.
Outstanding wear resistance, impact resistance, and fatigue resistance.
Good heat resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation.
Disadvantages
Nylon has a high water absorption rate, which may lead to dimensional changes and performance degradation. Additionally, nylon is sensitive to ultraviolet radiation, prolonged exposure to sunlight may cause aging, discoloration, and performance reduction. During processing, nylon has poor heat stability, making it prone to thermal decomposition and smoke generation.
Applications
In the automotive industry, nylon is used for engine components, fuel system parts, transmission system components, etc., to improve vehicle performance and safety. In the electronics and electrical fields, nylon is used to manufacture connectors, insulation materials, switches, and other components.
If you find yourself perplexed about selecting the right material for your plastic CNC machining project and are unsure which plastic material best suits your needs, feel free to reach out to Boyi for assistance at any time.
Related: Materials Guide
Put your plastic parts into production today
All uploads are secure and confidential.
How Are Plastics Parts Machined?
The processing of plastic parts involves using computer-controlled machines to remove portions of plastic polymers to form the desired products, including CNC turning, CNC milling, and CNC drilling, among others. The choice of these processes depends on the required material, product shape, and production needs.
CNC Turning
CNC turning is a process whereby excess material is removed from plastic polymers by rotating them and using cutting tools to achieve the desired shape of the parts. This process is particularly suitable for machining cylindrical or rotationally symmetric plastic parts.
During turning, special attention needs to be paid to the selection of cutting tool angles and feed rates to ensure machining precision and surface quality. To achieve better surface smoothness, polishing treatment can be applied to the workpiece surface.
CNC Milling
CNC milling, unlike CNC turning, is a process where excess material is removed from plastic polymers by rotating cutting tools while the plastic polymer is held stationary. CNC milling machines are typically equipped with multi-axis control systems, allowing the tools to move in multiple directions, enabling high-precision machining of complex-shaped parts, such as flat and irregularly shaped components.
When selecting milling processes, carbon tools can be used for machining carbon or glass-reinforced thermoplastics. To enhance machining efficiency, fixtures can be utilized to increase spindle speed. Additionally, to reduce stress concentration and improve the durability of parts, radii can be created at internal corners during design.
CNC Drilling
CNC drilling is a process that involves drilling holes in plastic materials using drill bits. Depending on the type and shape of the drill bit, holes of different cross-sections and sizes can be formed. In addition to drilling operations, CNC drilling machines can also perform some simple milling and turning operations.
When drilling, it is important to choose sharp drill bits to ensure machining quality and avoid applying excessive pressure to the workpiece. Additionally, to ensure smooth chip removal and prevent heat buildup, the correct drill bit should be selected, and a cooling system should be used.
How To Achieve A Perfect Finish On Plastic Parts?
Achieving perfect surface finishing for plastic parts is a complex and meticulous process that requires consideration of multiple factors, including material characteristics, machining processes, and post-processing techniques. Here are some key steps and guidelines to help you achieve high-quality surface treatment results:
- Avoid using cutting tools with complex geometries during the machining process to reduce surface defects caused by tool shapes.
- Ensure that plastic materials are properly and securely fixed during machining to avoid surface imperfections caused by material vibrations.
- Different plastic materials have different machining characteristics, so parameters need to be adjusted according to the properties of the material.
- Use a series of post-processing techniques to further improve the surface smoothness of plastic parts. This may include annealing, sandblasting, powder coating, etc. (Consideration can also be given to using some advanced surface finish techniques such as In-Mold Decoration (IMD), NCVM non-conductive vacuum metallization, and electroplating.)
For optimal surface treatment results, you can contact Boyi to learn how to choose the perfect finish machining technology for your product.
Put your plastic parts into production today
All uploads are secure and confidential.
Alternatives To Plastic CNC Machining
In addition to CNC machining, there are also some other rapid prototyping processes that can be used as alternative solutions for processing plastic parts. Common examples include:
Plastic Injection Molding

Injection molding is a process where pelletized plastic is melted, then injected into a mold under high pressure, and upon cooling, the corresponding parts are obtained. It can process flexible materials such as TPE and rubber.
One of the advantages of injection molding is the repeatability between batches. Molds can withstand millions of parts with minimal wear, allowing parts from one batch to the next to be nearly identical. Additionally, injection-molded parts require minimal additional work or surface finishing.
3D Printing
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process where various prototypes or batch components with unique shapes are produced by sintering powder according to CAD files. Common plastic 3D printing methods include SLS and SLA, which can be used for processing thermoplastic plastics such as nylon, PLA, ABS, and ULTEM.
SLS 3D printing: Utilizes lasers to fuse powder materials into components, and the entire printing process does not require additional support materials. It is suitable for movable parts or functional components in prototypes.
SLA 3D printing: Uses ultraviolet light to selectively cure photosensitive polymers layer by layer to create objects. It is suitable for demonstration prototypes, concept prototypes, or transparent/semi-transparent prototypes.
Each technology involves creating a 3D digital model and layer-by-layer construction of the desired parts. It is similar to plastic CNC machining, although it generates less material waste. However, 3D printing does not rely on traditional cutting tools, making it particularly suitable for manufacturing parts with complex designs that are difficult to achieve through traditional machining methods.
Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting is a technique that utilizes an existing pattern to create a silicone mold under vacuum conditions. Materials such as PU, silicone, nylon, ABS, etc., are then poured into the mold under vacuum conditions to clone replicas identical to the original pattern. Its replication accuracy can reach 99.8%, making it ideal for manufacturing high-precision parts.
Why Do People Prefer CNC Plastic Machining Over Other Methods?
Nowadays, many people like the ability of plastic CNC machining, for the following reasons:
Precision and Accuracy
The plastic parts processed by CNC have always been known for their accuracy. Plastic CNC machining uses computer programs to control the movement trajectory of cutting tools, achieving precision in every cut.
Complex Parts Production
CNC can process many plastic parts with complex surfaces. Although 3D printing technology can manufacture parts with complex designs, CNC machining is often more reliable in some applications that require extremely high precision.
Flexibility
Plastic CNC machining does not require the remaking of molds or changing equipment. Once the programming is set up, it can be used to process different products, demonstrating strong adaptability.
Strict Tolerances
CNC machining can achieve very high precision, usually up to a few micrometers or even smaller dimensions, ensuring consistency and precision in machining quality, thus meeting the manufacturing needs of high-precision and high-quality products.
Compatible With Different Plastic Polymers
CNC machining technology can effectively handle the physical and chemical properties of various plastic polymers through precise cutting and forming processes. Especially for tough plastic materials, their processing effect is even more outstanding.

Industrial Applications of Plastic CNC Machining
Plastic CNC machining has a wide range of applications in multiple industries, mainly due to its high precision, high efficiency, and wide material compatibility. The common industrial applications of this process include:
Household Appliance Industry
Plastic CNC machining can handle various plastic materials required for household appliance products, such as ABS, PC, PA, etc. It is used to manufacture shells and structural components for various household appliances. For example, the shells and heated parts of products like rice cookers and irons can be efficiently manufactured using CNC machining’s high precision and efficiency.
Automotive Industry
Plastic CNC machining enables the precise cutting and shaping of plastic components inside automobiles, such as dashboards, seat brackets, etc. These components need to withstand various stresses and vibrations during vehicle operation, hence requiring materials with sufficient strength and toughness.
Medical Industry
Due to the high precision and safety requirements of the medical industry, CNC plastic machining is currently used to manufacture medical mechanical parts such as prosthetics, diagnostic equipment, artificial hearts, implants, etc. Plastic CNC machining ensures compliance with complex safety standards.
When to Choose Plastic CNC Machining?
In these scenarios, plastic CNC machining may be the optimal choice:
Low volume or custom production: Plastic CNC machining is well-suited for small batch parts requiring quick turnaround or customized parts tailored to specific needs. Its high precision and flexibility enable rapid and cost-effective production of parts that meet particular requirements.
Complex shapes and features: Plastic CNC machining can handle various complex three-dimensional shapes and internal features such as grooves, holes, threads, etc. This makes it an ideal choice for manufacturing parts with intricate geometries.
Integration with metals or other materials: In certain applications, there may be a need to combine plastic parts with metals or other materials. Since CNC machining can work with multiple materials, it allows for convenient manufacturing of such assemblies.
Conclusion
In summary, plastic CNC machining indeed holds significant advantages in manufacturing plastic parts, especially when dealing with parts designed with strict tolerances, which other machining methods may struggle to match. However, selecting the right machining technology can be a challenging task, which is why outsourcing this work to a professional plastic CNC service provider is a wise choice.
Boyi, as a company providing customized plastic CNC machining services, not only offers a variety of plastic materials suitable for CNC machining but also ensures the quality and performance of the selected materials meet customer requirements through a rigorous and streamlined selection process. Additionally, Boyi engineering team possesses extensive experience and professional knowledge, enabling them to provide customers with expert material selection advice and design suggestions to optimize product designs and enhance machining efficiency and quality.
If you are seeking a professional plastic CNC machining service provider, Boyi would be your best choice. We are committed to providing you with high-quality services to help you achieve your goals in product design and manufacturing.
Put your plastic parts into production today
All uploads are secure and confidential.
FAQ
POM produces less built-up edge during machining compared to other plastics, making it ideal for achieving high precision and fine surface finishes. These characteristics make POM a popular choice for CNC machining applications across various industries.
Some commonly used hard plastics for CNC machining include Acetal (POM), Polycarbonate (PC), and Acrylic (PMMA). Acetal offers excellent mechanical properties and dimensional stability, making it suitable for precision parts.
Tagged: CNC Machining Guide